With Blue Origin launching its fourth space mission, Virgin Galactic completing its first manned missions, and SpaceX launching several reusable rockets, space is trully the final frontier that corporations can monopolise. We are effectively on the verge of blurring the lines between science fiction and reality, as corporations around the world race to stay ahead in the battle for supremacy in the space wars that have only recently begun. Indeed, the galactic rush is characterised by large corporations and nations rapidly advancing toward gaining control of not just space but dominating control over data and others.
The race to dominate space has resulted in several countries claiming to have the most extensive space programmes, including the United States, China, and others. The United States hopes that the $100 million Artemis programme will send humans to the moon by 2025, and China hopes to establish a lunar base with a European nation by 2027. Separately, China plans to launch 40 space missions, six of which will be manned.
The main motivation has unquestionably been the speed and number of manned missions for the future of travel. This includes efforts to dominate terrestrial activities, weapons, and other tools needed to disrupt and damage satellites that are sprouting up all over the world.
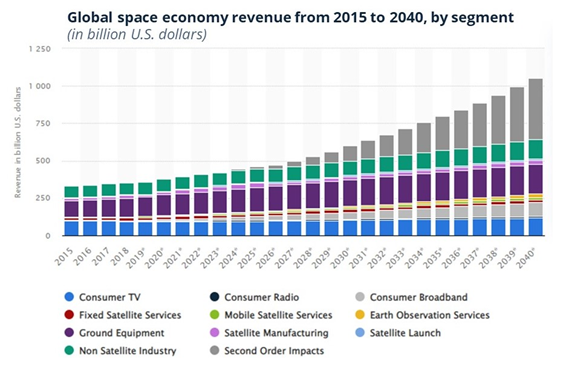
While the age-old battle for global dominance intensifies via satellites, the private sector, including billionaires, is rapidly straddling satellite communications, observational statistics, space research, and other areas. And the space economy is expected to be worth $1.25 trillion within a few decades, with the satellite infrastructure market alone worth around $570 billion.
In a virtual 5G and cloud-based world, an infinite demand for data will catapult the space economy. Even before the global financial crisis, broadband internet-enabled satellites were on the rise as a means of providing better mobility solutions. Global corporations, including several governments, are also attempting to increase the conversion of hardware-based solutions to application-based solutions for daily use. Countries and corporations have bombarded space with satellites as the race to control the majority of space heats up. The world’s reliance on space satellites to support the smooth operation of global economies is increasing.
On the one hand, the West has seen large corporations and countries compete to be the first to establish the largest market share of space. Countries such as Japan, on the other hand, have developed methods for docking and removing space debris. As there are over 3000 inactive satellites on the planet and tens of thousands of debris that could harm an active satellite, clearing space debris will become one of the most important businesses. Japanese automaker Honda too, plans to launch a company by 2030 that will develop a small rocket capable of carrying satellites weighing less than a ton
However, the rapid advancement towards commercial space travel in 2022 has revealed what the current decade will be like. Eventually, the advantages of increased competition in any industry trickle down to securing a spot among future astronauts. According to a recent report, entry into the lauded space club can be purchased for as little as $450,00 on Virgin Galactic. It remains to be seen when space travel will be as easily booked as regular passenger airlines or trains.



